[DS] 3. Foundations of Machine Learning
Machine Learning and Linear Regression
예제: 내일 서울의 peak power consumption을 구해라.
- scatter를 찍어본다.
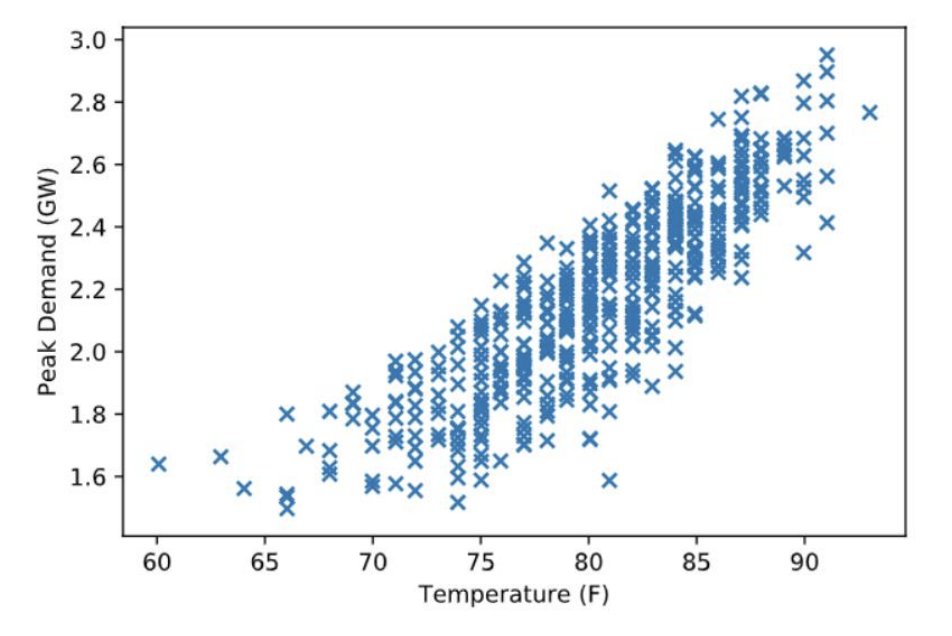 뭔가 선형으로 나올 것 같음
뭔가 선형으로 나올 것 같음 -
Hypothesis: Linear model Linear model일 것이라 가정하고 선을 그려봄
Peak_Demand $\approx \theta_1 \cdot$ High_Temperature $+ \theta_2$
$\theta_1$: slope(기울기) $\theta_2$: intercept(절편) -
Making Predictions 내일에 관한 prediction을 만들어야 한다. 내일 최대 온도가 72도라고 가정하면,
Predicted_Peak_Demand $\approx \theta_1 \cdot 72 + \theta_2 = 1.821 GW$ -
Linear Model 구한 선의 결과와 실제 값의 차이를 minimize 시켜야함
(e.g. squared loss) $E(\theta) = \sum_{i\in days}(\text{Predicted_Peak_Demand}^{(i)} - \text{Peak_Demand}^{(i)})^2$
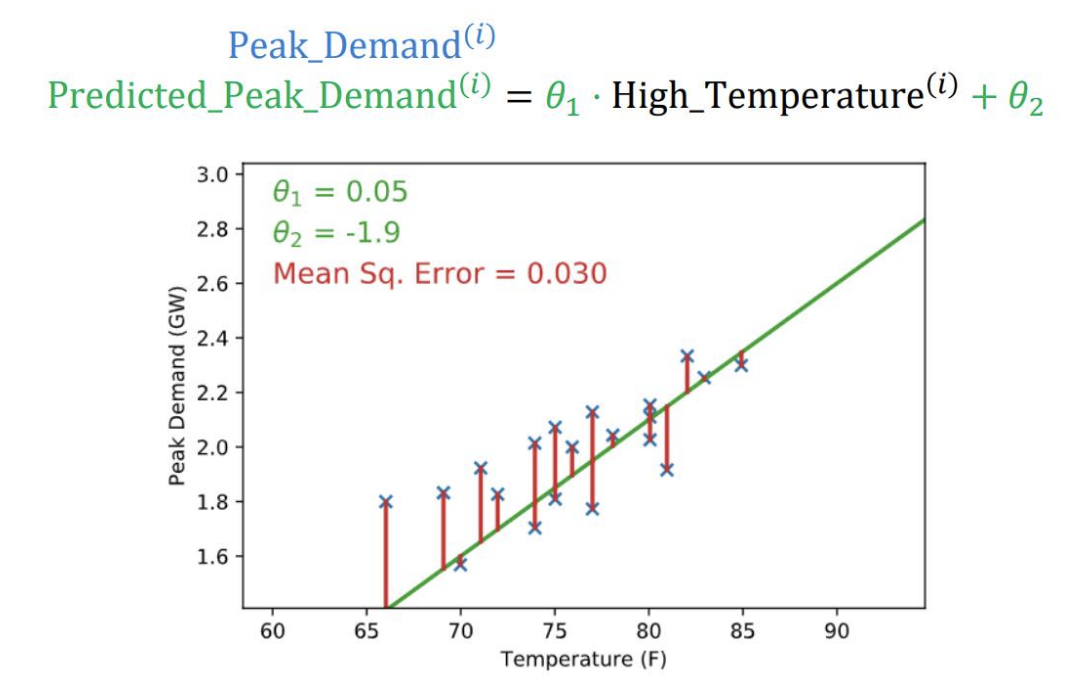 Mean Sq. Error: Minimize 해야하는 궁극적인 목적 함수, Object Function, Loss function
Mean Sq. Error: Minimize 해야하는 궁극적인 목적 함수, Object Function, Loss function - Finding parameters Function을 Minimize하는 $\theta_1, \theta_2$를 구해야함
\begin{align}
E(\theta) = E(\theta_1, \theta_2) &= \sum_{i\in days}(\theta_1 \cdot \text{High_Temperature}^{(i)} + \theta_2 -\text{Peak_Demand}^{(i)})^2 \nonumber \newline &\equiv \sum_{i\in days}(\theta_1 \cdot x^{(i)} + \theta_2 - y^{(i)})^2\nonumber
\end{align}
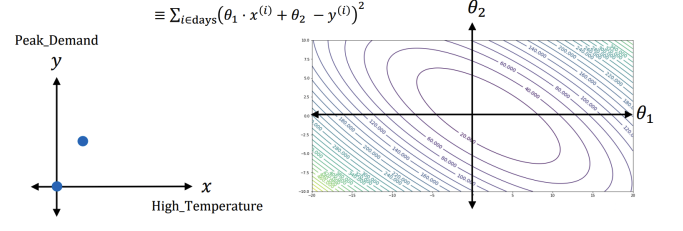
-
solution space
Gradient descent
좋은 $\theta$값을 찾기 위해서 다음 과정을 반복:
\begin{align} \theta_1 &:= \theta_1 - \alpha \frac{\partial}{\partial \theta_1}E(\theta_1, \theta_2) \nonumber\newline \theta_2 &:= \theta_2 - \alpha \frac{\partial}{\partial \theta_1}E(\theta_1, \theta_2) \nonumber\newline \end{align}
함수값이 큰 값이 나오기 때문에 Gradient가 마이너스가 되는 방향으로 Update해줘야함 Gradient는 Parameter의 Dimension만큼 나온다.
Machine Learning Notation
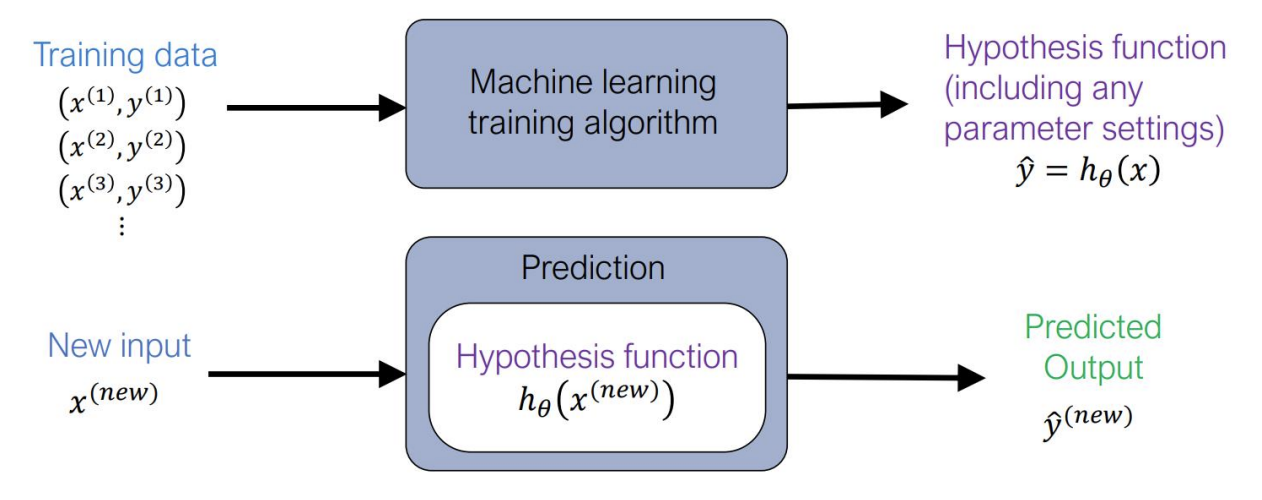
$h_\theta$를 찾아야함
- The canonical machine learning optimization problem
$\underset{\theta}{\text{minimize}} \sum_{i=1}^{m}\ell(h_\theta (x^{(i)}), y^{(i)})$
$y^{(i)}$: output
$x^{(i)}$: input
$h_\theta$: Hypothesis function
Linear Regression Revisited
Gradient in Linear Algebra Notation
Notation
\begin{align}
E(\theta) &= \sum_{i=1}^{m}(\sum_{j=1}^{n} \theta_j \cdot x_j^{(i)} - y^{(i)})^2 \nabla_{\theta}E(\theta) &= 2\sum_{i=1}^{m} x^{(i)}(x^{(i)^{T}}\theta - y^{(i)})
\end{align}
Maximum likelihood Estimation
Exam score Data point 75, 80, 90이 들어왔다고 가정.
이 데이터를 가장 잘 표현할 수 있는 Gaussian(정규분포) 모델은?
Gaussian의 parameter? 평균, 표준 편차
평균과 편차를 가지고 있을 때, 데이터 샘플들이 이렇게 나올 확률?
= 각각 데이터 포인트들이 이 모델 분포에서 나왔을 확률을 다 곱하면 된다!
$p(x^{(1)}, …, x^{(m)}; \theta) = \prod_{i=1}^{m} p(x^{(i)}; \theta)$
Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE): 위의 확률을 최대화 시키는 파라미터를 찾는다
$\underset{\theta}{\text{maximize}} \prod_{i=1}^{m} p(x^{(i)}; \theta)$
그런데 하나하나 다 곱하기에는 로드가 너무 크기 때문에 Log를 씌운다..
$\underset{\theta}{\text{maximize}} \prod_{i=1}^{m} p(x^{(i)}; \theta) \equiv \underset{\theta}{\text{maximize}} \sum_{i=1}^{m} \log p(x^{(i)}; \theta) $
로그를 씌우니 전체를 곱하는 것 -> 전체를 더하는 것으로 바뀜!
MLE for Bernoulli
이항분포에서 MLE 사용
$\underset{\theta}{\text{maximize}} \sum_{i=1}^{m} (x^{(i)} \log \phi + (1-x^{(i)}) \log(1-\phi))$
$\phi$에 대하여 미분을 하면?
$\frac{d}{d\phi}\ell(\phi) = \sum_{i=1}^{m} (\frac{x^{(i)}}{\phi} - \frac{1-x^{(i)}}{1-\phi}) = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^{m} x^{(i)}}{\phi} - \frac{\sum_{i=1}^{m} (1-x^{(i)})}{1-\phi}$
log 함수를 미분?
log함수를 미분하면 기본적으로 다음과 같이 된다. $\frac{d}{dx}\log x = \frac{1}{x}$
그러나 $1-x$를 미분하면, 마이너스가 튀어 나오게 된다!!
$\frac{d}{dx}\log (1-x) = \frac{-1}{1-x}$
Chain rule에 의해서 로그를 미분한 후 나온 $\frac{1}{1-x}$를 한번 더미분 해주어야 하기 때문….