[DS] 1. Mathematical Preliminaries
Basic probability & statistics
Probability (확률)
likelihood of events 이벤트의 가능성
The probalitiy $p(s)$ of an outcome s satisfies:
- $0 \leq p(s) \leq 1$: 확률은 0~1의 값을 가진다.
- $\sum_{s\in S} p(s) = 1$: 모든 event의 합을 더했을 때 1이 되야함
Probability vs. Statistics
확률 vs. 통계
Probability: predicting the likelihood of future events
Event가 발생할 확률, 정도
예측하는데 주로 사용
Statistics: analyzes the frequency of past events
이전에 발생했던 event들을 분석
데이터를 보고 분석하는데 주로 사용
Compound Events and Independence
- event A: 학생들 중 절반이 여성이다.
- event B: 절반 이상의 학생이 중앙값을 넘는다.
이때 학생이 A이자 B일 확률은?
Events A와 B가 각각 독립적일 때
- $P(A \cap B) = P(A) \times P(B)$
독립적인 가설은 계산할때는 편리하지만, 실제로 예측하는데는 좋지 않다.
하지만 자주 사용됨.
Conditional Probability
B 사건이 일어났을 때 A사건이 일어날 확률 ($P(A\vert B)$)
- $P(A\vert B) = \frac{P(a\cap b)}{P(B)} = \frac{\text{A와 B가 발생할 경우의 수}}{\text{B가 발생할 경우의 수}}$
두 사건이 서로 Independent하다면, $P(A\vert B)$는 $P(A)$ 가 된다.
Bayes Theorem
베이즈 정리
- $P(B\vert A) = \frac{(P(A\vert B)P(B))}{P(A)}$
$P(A\cap B)$: 두 사건 A와 B가 발생할 확률
$P(A)$: A가 발생할 확률
$P(B\vert A)$: A가 발생하였을 때 B가 발생할 확률
- $P(A\cap B) = P(A)P(B\vert A)$
- $P(A\cap B) = P(B)P(A\vert B)$
- $P(A)P(B\vert A) = P(B)P(A\vert B)$
- $P(A\vert B) = P(A)\frac{P(B\vert A)}{P(B)}$
$P(A\vert B)$: 사후 확률(Posterior probability), 사건 B가 발생했을 때 사건 A가 발생하는 조건부 확률
$P(B\vert A)$: 가능도(likelihood), 사건 A가 발생했을 때 사건 B가 발생하는 조건부 확률
$P(A)$: 사전 확률(prior) H(hypothesis), 사건 A가 발생할 확률
$P(B)$: 증거(evidence) E(evidence), 사건 B가 발생할 확률
Example
질병 A의 발병률은 0.1%. 이 지병이 실제로 있을 때 질병이 있다고 검진할 확률 (민감도; sensitivity)은 99%, 질병이 없을 때 실제로 질병이 없다고 검진할 확률 (특이도; specificity)는 98%
어떤 사람이 질병에 걸렸다고 검진 받았을 때, 정말 질병에 걸렸을 확률?
Hypothesis: True(실제로 병이 있다)
Evidence: Positive (병이 있다고 진단을 받았다)
- $P(H) = 0.001$: 실제로 병이 있을 확률
- $P(E\vert H) = 0.99$: 실제로 병이 있을 때 병이 있다고 판단할 확률
- $P(E) = $병이 있는데 병이 있다고 진단 받을 확률 + 병이 없는데 병이 있다고 진단 받을 확률 = 0.99 + 0.02 = 1.01$
- $P(E^c\vert H^c) = 0.98$
- $P(H\vert E) = \frac{P(E\vert H)P(H)}{P(E)} = \frac{P(E\vert H)P(H)}{P(E)} = \frac{0.99 \times 0.001}{1.01} = 0.0098…$
따라서 0.98%
Sensitivity and Specificity
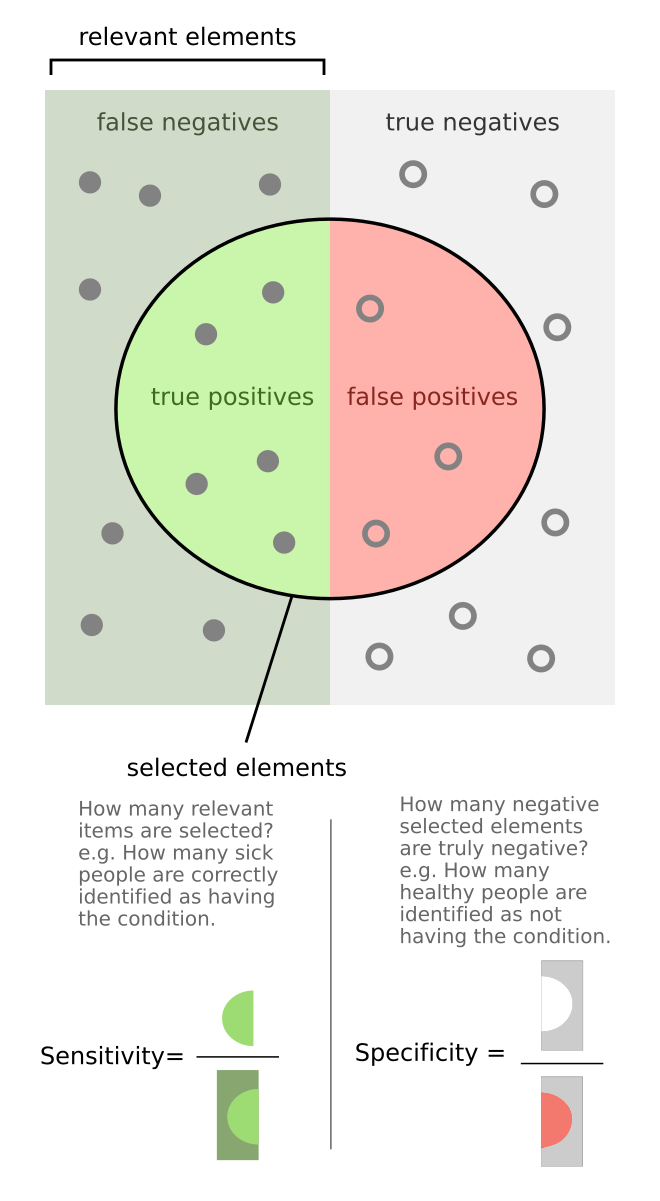
왼쪽: positive samples
오른쪽: negative smaples
원: positive라고 예측한 부분
일 때,
True positive: True라고 예측한 부분이 True가 맞음
False positive: True라고 예측한 부분이 False
True negative: False라고 예측한 부분이 True
False negative: False라고 예측한 부분이 False가 맞음
여기서 Sensitivity(민감도)란, $\frac{\text{True positive}}{\text{positive samples}}$
Specificity(특이도)란, $\frac{\text{False negative}}{\text{negative samples}}$
Distruibutions of Random Variables
확률 변수의 분포
- Probability density functions (PDFs, 확률 밀도 함수)

histogram일 때도 있고, continous한 모델일 수도 있음. 각각 Entry 값들 (Random variable)의 합이 1이고, 각각의 값들이 0~1 사이의 값을 가짐.
Probability/Cumulative Distributions
CDF(cumulative distribution function; 누적 분포 함수): PDF의 합을 구함
- $C(X \leq k) = \sum_{x\leq k} P(X=x)$
Descriptive Statistics
- Central tendency measures (중심 경향 측정)
- mean(평균값): meaningful for symmetric distributions without outliers (특이점이 없는 대칭 분포에 의미가 있음) e.g., height and weight
- median(중앙값): better for skewed distributions or data with outliers (skewness distributions(왜곡된 분포) 또는 노이즈가 많이 껴있는 곳에 더 좋음) e.g., wealth and income
- Variation or variability measures
- variance(분산): square of the standard deviation(표준편차의 제곱)
- $\hat{\sigma}=\sqrt{\frac{\sum_{i}^{n}(x_i-\bar{x})^2}{n-1}}$
- variance(분산): square of the standard deviation(표준편차의 제곱)
Aggregation as Data Reduction
Representing a group of elements by a new derived element, like mean, min, count, sum reduces a large dataset to a small sumamry statistic
큰 데이터 셋 -> 작은 통계로 줄어듬
Such statistics can become features when taken over natural groups or clusters in the full data set
이러한 통계는 features로 연계될 수 있다.
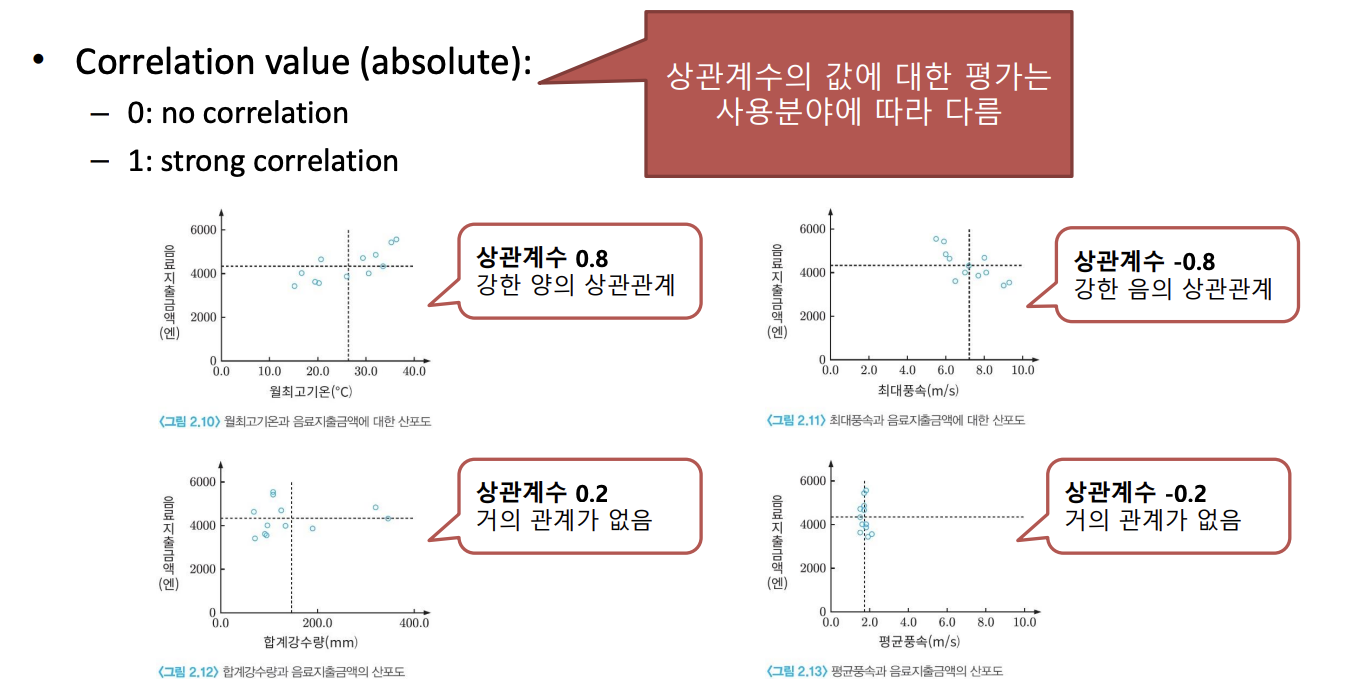
Correlation Analyses
Correlation 분석: 2개의 변수 간에 선형적인 관계를 파악하고 싶을 때 사용 (어느정도 관계가 있는 지)
Causal relationship(인과관계)를 나타내는 것은 아님! i.e., prediction model에 사용할 수 없음
Histogram
 Random vaiable을 만들 때 자주 사용됨
Random vaiable을 만들 때 자주 사용됨
- “bin”: range of values (막대그래프의 폭)
-
Quantization (이산화 과정)
- Effect of number of bins
- Accurate assessment of distribution
분포에 대한 정확성을 평가함 - Computational complexity
- kernel-based non-parametric PDF estimation (histogram or Parzen window)
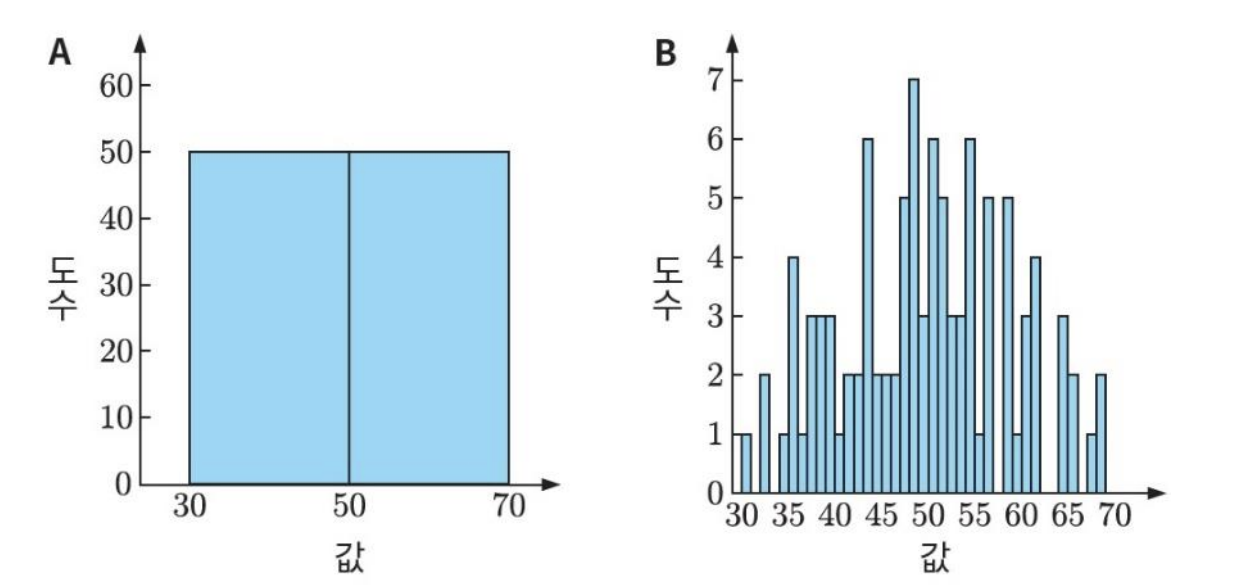
분포를 표현하는 데에 영향을 끼침
적당한 bin size를 찾는 것이 중요함
- kernel-based non-parametric PDF estimation (histogram or Parzen window)
- Accurate assessment of distribution
Historgram은 frequency (probabilistic distribution)을 의미하는 것이지 correlation을 의미하는 것이 아니다.
Correlation Coefficient (상관 계수)
- $Corr_{XY} = \frac{Var(XY)}{\sigma_X \sigma_Y}$
- $Var(XY)$: covariance of X and Y (X와 Y의 공분산)
- $\sigma_X$: standard deviation of X (X의 표준편차)
- $\sigma_Y$: standard deviation of Y (Y의 표준편차)
Vector and Matrices
Vector
Vector: 값들의 1D array
Notation $x \in \mathbb{R}^n$ 대부분의 Vector는 아래와 같은 형태로 (세로로) 표현
\begin{align}
x &= \begin{bmatrix}
x_1 \newline
x_2 \newline
\vdots \newline
x_n
\end{bmatrix} \nonumber
\end{align}
$x^T = [x_1, x_2, …, x_n]$, Transpose는 행과 열을 바꾸는 것이기 때문에 가로로 작성
Matrices
Matrix: 값들의 2D array Notation $A \in \mathbb{R}^{m\times n}$ \begin{align} A &= \begin{bmatrix} &A_{11} &\ldots &A_{1n} \newline &\vdots &\ddots &\vdots \newline &A_{m1} &\ldots &A_{mn} \end{bmatrix} \nonumber \end{align}
tabular data(table 형태로 표현되는 데이터)를 저장할 때 사용
Example
“Grade” table:
| Person ID | HW1 Grade | HW2 Grade |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 100 | 80 |
| 6 | 60 | 80 |
| 100 | 100 | 100 |
이 데이터(primary key를 무시) Matrix로 표현하면
\begin{align} A \in \mathbb{R}^{3\times 2} = \begin{bmatrix} &100 &80 \newline &60 &80 \newline &100 &100 \end{bmatrix} \nonumber \end{align}
- Row major ordering: 100, 80, 60, 80, 100, 100
- Column major ordering: 100, 60, 100, 80, 80, 100
Higher dimensional matrices
“Higher dimensional matrices”는 Tensor라고 부른다.
Basic of linear algebra
아래 식을 vector matrix form으로 작성하면?
\begin{align} 4x_1-5x_2&=-13 \nonumber \newline -2x_1+3x_2&=9 \nonumber \end{align}
$Ax=b$ \begin{align} \text{where, } A= \begin{bmatrix} 4 &-5 \newline -2 &3 \end{bmatrix} , b = \begin{bmatrix} -13 \newline 9 \end{bmatrix}, \text{and } x = \begin{bmatrix}x_1 \newline x_2 \end{bmatrix} \nonumber \end{align}
Basic Matrix Operations
- For $A, B \in \mathbb{R}^{m \times n}$, matrix addition/subtraction은 just the elementwise(각 요소 끼리만) addition/subtraction한다:
- $C \in \mathbb{R}^{m \times n} = A+B \Leftrightarrow C_{ij} = A_{ij}+B_{ij}$
- For $A \in \mathbb{R}^{m \times n}$, transpose is an operator that “flips” rows and columns (transpose는 행과 열을 뒤집음):
- $C \in \mathbb{R}^{m \times n} = A^T \Leftrightarrow C_{ji} = A_{ij}$
- For $A \in \mathbb{R}^{m \times n}, B \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times p}$ matrix multiplication(곱셈) is defined as
- $C \in \mathbb{R}^{m \times p} = AB \Leftrightarrow C_{ij} = \sum_{k=1}^{n} A_{ik}B_{kj}$
- Matrix multiplication is associative, distributive, but not commutative (size의 제약이 있기 때문)
- $A(BC) = (AB)C \quad A(B+C)=AB+AC \quad (AB \neq BA)$
Matrix Inverse
Identity matrix: 대각 행렬만 다 1인 Matrix ($i==j?1:0lms$)
Identity matrix는 commutative하다.
Inverse matrix: 어떤 matrix에 Inverse matrix를 곱했을 때 Identity matrix가 나오는 Matrix
$A \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}, A^{-1} \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}$
$AA^{-1} = I = A^{-1}A$: commutative
이전에 나왔던 식 $Ax=b$를 inverse matrix를 사용해서 표연하면 간단하게 작성할 수 있다.
$x = A^{-1}b$
Some Miscellaneous Definitions/Properties
- Transpose of matrix multiplication (Matrix 곱의 transpose), $A\in \mathbb{R}^{m \times n}, B \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times p}$
- $(AB)^T = B^TA^T$
- Inverse of product (Matrix 곱의 inverse), $A\in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}, B \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}$
- $(AB)^{-1}= B^{-1}A^{-1}$
- Inverse of product (Matrix 곱의 inverse), $A\in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}, B \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}$
- $(AB)^{-1}= B^{-1}A^{-1}$
- Inner product: for $x, y \in \mathbb{R}^n$
- $x^Ty \in \mathbb{R} = \sum^{n}_{i=1}x_iy_i$
- Vector norms: for $x \in \mathbb{R}^n$, we use $||x||_2$ to denote Euclidean norm
- $||x||_2 = (x^Tx)^{\frac{1}{2}}$
Norm? Size of Vector
- $L_1$ Norm ($L_2$ Norm과 함께 주로 사용): 절대값의 합
- $||x||_1 = \sum|x_i|$
- $L_2$ Norm (일반적으로 사용): 제곱의 합을 sqrt
- $||x||_2 = \sqrt{\sum x^2_i} = (x^Tx)^{\frac{1}{2}}$
- $L_p$ Norm
- $||x||_p = \sqrt[p]{\sum|x_i|^p}$
- $L_\infty$ Norm
- $||x||_\infty = max(|x_1|, |x2|, …, |x_n|) = \sup_i|x_i|$
Brief vector calculus
Vector Derivative
Vector by scalar
(Vector를 scalar로 미분): 모든 원소를 스칼라로 미분
$y = [y1, y2, …, y_m]^T$일 때
\begin{align}
\frac{\partial y}{\partial x} &= \begin{bmatrix}
\frac{\partial y_1}{\partial x} \newline
\frac{\partial y_2}{\partial x} \newline
\vdots \newline
\frac{\partial y_m}{\partial x}
\end{bmatrix} \nonumber
\end{align}
Scalar to Vector
(Scalar를 Vector로 미분): 벡터 각각에 편미분 = gradient라고 함
$x = [x1, x2, …, x_n]^T$일 때
$\frac{\partial y}{\partial x} = [\frac{\partial y}{\partial x_1}, \frac{\partial y}{\partial x_2}, …, \frac{\partial y}{\partial x_n}]$
\begin{align}
\nabla f &= \begin{bmatrix}
\frac{\partial f}{\partial x_1} \newline
\frac{\partial f}{\partial x_2} \newline
\vdots \newline
\frac{\partial f}{\partial x_n}
\end{bmatrix} \nonumber
= (\frac{\partial f}{\partial x})^T
\end{align}
Vector to Vector
(Vector를 Vector로 미분): 각각의 원소끼리 미분 => Matrix가 된다! (Jacobian matrix)
$x = [x1, x2, …, x_n]^T, y = [y1, y2, …, y_m]^T$일 때
$\frac{\partial y}{\partial x} = [\frac{\partial y}{\partial x_1}, \frac{\partial y}{\partial x_2}, …, \frac{\partial y}{\partial x_n}]$
\begin{align}
\frac{\partial y}{\partial x} = \begin{bmatrix}
\frac{\partial y_1}{\partial x_1} &\frac{\partial y_1}{\partial x_2} &\ldots &\frac{\partial y_1}{\partial x_n} \newline
\frac{\partial y_2}{\partial x_1} &\frac{\partial y_2}{\partial x_2} &\ldots &\frac{\partial y_2}{\partial x_n} \newline
\vdots &\vdots &\ddots &\vdots \newline
\frac{\partial y_m}{\partial x_1} &\frac{\partial y_m}{\partial x_2} &\ldots &\frac{\partial y_m}{\partial x_n}
\end{bmatrix} \nonumber
\end{align}
Vector Calculus (Derivatives): PCA
Principal component analysis (PCA, 주성분 분석)
 데이터의 차원을 축소 시켰을 때 정보량의 손실이 가장 적은 방향(Vector)을 찾고 싶다
데이터의 차원을 축소 시켰을 때 정보량의 손실이 가장 적은 방향(Vector)을 찾고 싶다
$X = {(x_i, y_i, z_i)^T | i=1, …, n}$
- 각각의 Data point는 3D-vector라고 생각함
- n: 요소의 개수
- $x_i, y_i, z_i$: 각각의 i번째 포인트의 값
$u = \frac{1}{n}\sum^n_{i=1}X_i$
- mean vector
$C = \frac{1}{n}\sum^{n}_{i=1} X_iX_i^T - uu^T$
- Covariance matrix